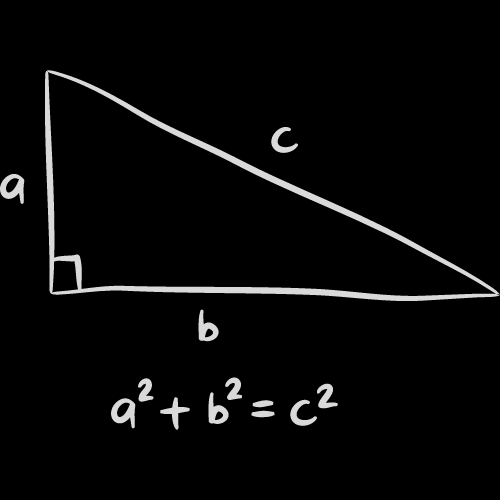
Pythagoras’ theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This can be written mathematically as:
c² = a² + b²
where c is the length of the hypotenuse, and a and b are the lengths of the other two sides.
Pythagoras’ theorem:-
This theorem is named after the ancient Greek mathematician Pythagoras, who is credited with its discovery. The theorem is used in many areas of mathematics and science, such as geometry, trigonometry, and physics.
There are many different ways to prove the Pythagorean theorem, but one of the most famous and elegant is geometric proof. The geometric proof is based on the area of squares, and it shows that the area of the square on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
Another way to prove the Pythagorean theorem is to use algebra. We can start by using the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle with sides of length a and b:
c² = a² + b²
We can rearrange this equation to solve for c:
c = √(a² + b²)
This gives us the length of the hypotenuse in terms of the lengths of the other two sides.
In summary, Pythagoras’ theorem is a fundamental result in geometry that relates the lengths of the sides of a right-angled triangle. The theorem can be proved in a variety of ways, and it has many applications in mathematics, science, and engineering.



0 Comments
If you have any doubts, please let me know...